Knapsack Problem - Theory, Algorithm, Example, Math for Computer Science Students
Knapsack problem demonstration - From (Sartaj Sahni Book):
There are n objects and a knapsack or bag. Object i has a weight wi and the knapsack has the capacity m. If a fraction xi, 0<=xi<=1, of object i is placed into the knapsack, then a profit of pixi is earned. The objective is to obtain a fiiling of the knapsack that maximizes the total profit earned. Since the knapsack capacity is m, we require the total weight of all chosen objects to be at most m. So, we can say the problem as below -
i = object
w = weight
m = capacity
maximize profit = ∑pixi
total weight = ∑wixi
The profits and weights will be the positive numbers
Algorithm Knapsack Problem (Sartaj Sahni Book):
Algorithm Greedy Knapsack(m, n)
// P[1:n] and W[1:n] contain the profit and the weight respectively
// of the n objectives such that P[i]/W[i] >= P[i+1]/W[i+1]
// m is the knapsack size and x[1:n] is the solution vector
{
for i = 1 to n do x[i] = 0.0
U = m;
for i = 1 to n do
{
if (W[i] > U) then break
x[i] = 1.0; U = U - W[i]
}
if (i <= n) then x[i] = U/W[i]
}
Math Example Knapsack Problem (Sartaj Sahni Book):
Example: Consider the following instances of Knapsack problem: n=3, m=20, (P1, P2, P3) = (25, 24, 15) and (W1, W2, W3) = (18, 15, 10). What are the feasible and optimal solution for this Knapsack problem?
Solution:
Feasible solutions are:
| x1 | x2 | x3 | wixi | pixi |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2 | 1/3 | 1/4 | 9+5+2.5 = 16.5 | 12+8+3.75 = 23.75 |
| 1 | 2/15 | 0 | 18+2+0 = 20 | 25+3.2+0 = 28.2 |
| 0 | 2/3 | 1 | 0+10+10 = 20 | 0+16+15 = 31.0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1/2 | 0+15+5 = 20 | 0+24+7.5 = 31.5 |
So, we can see there there are four feasible solutions but there is one solution where the profit maximize. The maximum profit is 31.5. So, this is the optimal solution for Knapsack Problem.
Optimal solution finding technique short-cut:
We may consider there is 3 Jobs because there is 3 weights. Jobs are J1, J2, J3.
J1 = P1/W1 = 25/18 = 1.38
J2 = P2/W2 = 24/15 = 1.6
J3 = P3/W3 = 15/10 = 1.5
So, here Job 1.6>1.5>1.38 and jobs priority is = J2>J3>J1
| x1 | x2 | x3 | wixi | pixi |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 1/2 | 0+15+5 = 20 | 0+24+7.5 = 31.5 |
Concept Theory from Wikipedia:
The knapsack problem or rucksack problem is a problem in combinatorial optimization: Given a set of items, each with a weight and a value, determine the number of each item to include in a collection so that the total weight is less than or equal to a given limit and the total value is as large as possible. It derives its name from the problem faced by someone who is constrained by a fixed-size knapsack and must fill it with the most valuable items.
Learn More about Knapsack Problem
Tags:
Knapsack Problem - Theory, Algorithm, Example, Math for Computer Science Students, Knapsack Problem example, Knapsack Problem Algorithm, Knapsack Problem Code, Knapsack Problem Math,
Data Mining. Concepts and Techniques, 3rd Edition Free Download.pdf
Book Name : Data Mining. Concepts and Techniques
Book Edition: 3rd Edition
Book Author : Jiawei Han, Micheline Kamber, Jian Pei
Book Download Link :
Download Link 1 - Download Data Mining Book From BDUpload
Download Link 2 - Download From Media Fire via Adf.ly
Download Link 3 -
Book Download Size - 12.5MB
Book Front Page -
So, Download Differential Equation Book By Clicking
Download Link 1 - Download Data Mining Book From BDUpload
Download Link 2 - Download From Media Fire via Adf.ly
Button.
Some Demo Pages
Of Data Mining. Concepts and Techniques, 3rd Edition Book Screenshot. Click download link1 or download link2 to downloadNote:
If you have face any problem to download Data Mining. Concepts and Techniques, 3rd Edition Free Download By Jiawei Han, Micheline Kamber, Jian Pei.pdf then comment below. A direct link of this book will send to you immediately.Tags:
Data Mining. Concepts and Techniques, 3rd Edition Free Download By Jiawei Han, Micheline Kamber, Jian Pei.pdf, Data Mining. Concepts and Techniques, 3rd Edition, Data Mining free pdf, data mining book download link, data mining concept and techniques book free download
বাংলায় সি প্রোগ্রামিং শিখুন - ৫৫ মিনিটের ভিডিও টিউটরিয়াল
আসসালামুআলাইকুম, আমি মনিরুজ্জামান আকাশ। পটুয়াখালি বিজ্ঞান ও প্রযুক্তি বিশ্ববিদ্যালয়ে কম্পিউটার বিজ্ঞান ও প্রকৌশল অনুষদে পড়ছি। এটা আমার ৪র্থ বর্ষ। আমার জীবনের প্রথম প্রোগ্রামিং শুরু সি প্রোগ্রামিং দিয়ে। তাই সি প্রোগ্রামিং এর প্রতি রয়েছে অসম্ভব ভালবাসা।
আচ্ছা, আজকে আমি আপনাদের সাথে সি প্রোগ্রামিং এর বেসিক বিষয়গুলো নিয়ে আলোচনা করব এবং সাথে সাথে রিয়েল-টাইম এক্সাম্পল দেখাব যাতে আপনাদের সি প্রোগ্রামিং পুরোপুরি বুঝতে, শিখতে সহজ হয়।
এই টিউটরিয়ালে আমরা যা যা দেখব-
- সি প্রোগ্রামিং এ্রর একটা কোড কিভাবে কাজ করে
- সি প্রোগ্রামিং ভ্যারিয়েবল
- সি প্রোগ্রামিং ডাটা টাইপ
- সি প্রোগ্রামিং ইনপুট-আউটপুট
- সি প্রোগ্রামিং ইফ-এলস
- সি প্রোগ্রামিং লুপ- for লুপ, while লুপ
- সি প্রোগ্রামিং এরে Array
সাথে আমরা যে যে এক্সাম্পলগুলো কাভার করার চেষ্টা করব সেগুলো হল-
- হ্যালো ওয়ার্ল্ড প্রোগ্রাম
- ইউজারের কাছ থেকে ইনপুট নিয়ে প্রিন্ট করার প্রোগ্রাম
- ছোট-বড় সংখ্যা বের করার প্রোগ্রাম
- জোড়-বিজোড় সংখ্যা বের করার প্রোগ্রাম
- টুটাল সামিং প্রোগ্রাম - for, while লুপ ব্যবহার করে
- এরেতে ভ্যালু ইনসার্ট, রিড, প্রিন্ট ইত্যাদি
সি প্রোগ্রামিং ভিডিও টিউটরিয়ালঃ
কোডসমুহঃ
Hello World Program Example
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
printf("Welcome To Our C Programming");
return 0;
}
Print Scan from Input C Program Example
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
int number;
float price;
double total_price;
//Give a number
printf("Enter a number = ");
scanf("%d", &number);
printf("Enter Product Price = ");
scanf("%f", &price);
printf("Enter total price = ");
scanf("%lf", &total_price);
printf("Number = %d\t Price = %.2f\tTotal Price = %.3lf\n", number, price, total_price);
}
If-Else Even, Odd C Program Example
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
int number;
printf("Please enter a number = ");
scanf("%d", &number);
//Positive or negative check
if (number > 0){
printf("Number is Positive\n");
}else if(number == 0){
printf("ooops... This is zero\n");
}
else{
printf("Number is Negative\n");
}
// Even Odd Check
if (number % 2 == 0){
printf("Even number\n");
}else{
printf("Odd number\n");
}
}
For Loop - Even,odd,Total Summation C Program Example
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
int number, i, sum = 0;
printf("Please enter upto number = ");
scanf("%d", &number);
//Even
printf("\nEven Numbers = ");
for(i = 0; i <= number; i = i+2){
printf("%d\t", i);
}
//Odd
printf("\nOdd Numbers = ");
for(i = 1; i <= number; i = i+2){
printf("%d\t", i);
}
//3 = 1+2+3 = 6
//Summing Using For Loop
for(i = 1; i <= number; i++){
sum = sum + i;
}
printf("\nTotal Summation = %d\n", sum);
}
While Loop - Even,odd,Total sum C Program Example
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
int number, i = 0, sum = 0;
printf("Please enter upto number = ");
scanf("%d", &number);
//Summing Using While Loop
while(i <= number)
{
sum = sum + i;
i++;
}
printf("\nTotal Summation = %d\n", sum);
}
Array - Array insert, read C Program Example
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
int number, i;
printf("Enter upto = ");
scanf("%d", &number);
int numbers[10000];
for(i = 0; i < number; i++){
printf("Element %d = ", i);
scanf("%d", &numbers[i]);
}
printf("Full numbers are = ");
for(i = 0; i < number; i++){
printf("%d\n", numbers[i]);
}
}
আশা করি ধৈর্য নিয়ে যদি ৫৫ মিনিটের এই টিউটরিয়ালগুলো শেষ করলে আপনি নিজেই সি প্রোগ্রামিং এর বাকিটা পথ আগাতে পারবেন, আর সেরকম ইন্সট্রাকশনও দেয়া আছে এখানে।
তারপর্ব যদি কোনো সমস্যা হয়, তাহলে আমার সাথে যোগাযোগ করবেন।
ফেইসবুকে আমি - Maniruzzaman Akash
ইমেইলে - manirujjamanakash@gmail.com
ইউটিউবে - Maniruzzaman-Akash
Python Code Example - Fibonacci Series in Python
Today we'll show how to get the Fibonacci number using Python Programming language. Fibonacci Series is on e of the most common data structure in Computer Science. We;ll just do it using Python programming language.
Code Part
n_string = input('How many fibonacci number do want to get = ')
n = int(n_string)
fib0 = 0
fib1 = 1
fib = 0
i = 0
while i < n:
fib = fib0+fib1
print(fib)
fib0 = fib1
fib1 = fib
i = i+1
Logic behind the Fibonacci Series
Two fixed Fibonacci numbers are = 0 1
And next will be generated from this.
0
1
0 + 1 = 1
1 + 1 = 2
2 + 1 = 3
3 + 2 = 5
5 + 3 = 8
....
That means the Fibonacci number will be first_number + second number.
Then, the first number will be second number and the second number will be Fibonacci number.
Code Explanation Line By Line
n_string = input('How many gibonacci number do want to get = ')
n = int(n_string)
In first two line, take input from user by input() method. Which returns a string. Then in second line just convert it to integer using int()
Now Define the first two fibonacci number and variables
fib0 = 0
fib1 = 1
fib = 0
i = 0
Now start loop of while until total number of taken from user reaches. and then just do what I've said in logic part.
That means the Fibonacci number will be first_number + second number.
Then, the first number will be second number and the second number will be Fibonacci number.
while i < n:
fib = fib0+fib1
print(fib)
fib0 = fib1
fib1 = fib
i = i+1Full Code + Output(pic)
Having any problem, just comment out here
Factorial Number generate C program Bangla Tutorials - সি প্রোগ্রাম দিয়ে কিভাবে ফ্যাক্টরিয়াল সংখ্যা বের করা যায় তার প্রোগ্রাম
আজকের সি প্রোগ্রামিং এক্সাম্পলটা একদম সহজ এবং বিগিনার লেভেলের একটি সি প্রোগ্রাম। এই প্রোগ্রামের মাধ্যমে আমরা মূলত সি প্রোগ্রামিং এর for loop টা ব্যাবহার করব এবং দেখব কিভাবে সি প্রগ্রামিং দিয়ে ইউজারের কাছ থেকে ইনপুট নিয়ে সেটার ফ্যাকটরিয়াল Number Generate করা যায়।
কোনো সংখ্যার ফ্যাকটরিয়াল বের করার লজিক
মনে করুন, আমি ইনপুট দিলাম ৫, তাহলে ফ্যাকটরিয়াল হবে - ১২০কিভাবে,
৫ * ৪ * ৩ * ২ * ১ = ১২০
আচ্ছা, তাহলে একটা লুপের মাধ্যমে যদি আমরা প্রথমে factorial ভ্যারিয়েবল এ ১ রাখব।
double factorial = 1;তারপর যত নাম্বার নিব তত পর্যন্ত লুপ ঘুরাই এবং প্রত্যেক বার factorial ভ্যারিয়েবল এর সাথে i কে গুন করি, তাহলে লুপ শেষ হওয়ার পর factorial ভ্যারিয়েবল এ পুরাপুরি গুন করার পর ফ্যাক্টরিয়াল টা স্টোর করে রাখবে।
for(i = 1; i <= number; i++)
{
factorial = factorial * i;
}এটার ভিডিও টিউটরিয়াল ইউটিউবে -
প্রোগ্রামটি বুঝতে কোনো সমস্যা হলে কমেন্ট করবেন।
কোড পার্ট
#include<stdio.h>
main()
{
int number;
double factorial = 1;
int i;
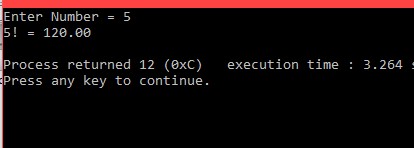
printf("Enter Number = ");
scanf("%d", &number);
for(i = 1; i <= number; i++)
{
factorial = factorial * i;
}
printf("%d! = %.2lf\n", number, factorial);
}
আউটপুটঃ
উইকিপিডিয়া থেকে ফ্যাক্টরিয়াল নাম্বার সম্পর্কে আরো পড়ুন - wikipedia.org/wiki/Factorial
ট্যাগসমূহঃ
C program factorial number bangla tutorial,C program factorial number code bangla tutorial, c programming bangla tutorials, সি প্রোগ্রাম ভিডিও টিউটোরিয়াল + কোড , সি প্রোগ্রামিং এক্সাম্পল, C programming factorial code, C programming factorial example code, C programming C programming code bangla tutorial,Even, Odd Number generate C program Bangla Tutorials - Factorial Number generate C program Bangla Tutorials - সি প্রোগ্রাম দিয়ে কিভাবে ফ্যাক্টরিয়াল সংখ্যা বের করা যায় তার প্রোগ্রাম
Even, Odd Number generate C program Bangla Tutorials - সি প্রোগ্রাম দিয়ে কিভাবে জোড় বিজোড় সংখ্যা বের করা যায় তার প্রোগ্রাম
আজকের সি প্রোগ্রামিং এক্সাম্পলটা একদম সহজ এবং বিগিনার লেভেলের একটি সি প্রোগ্রাম। এই প্রোগ্রামের মাধ্যমে আমরা মূলত সি প্রোগ্রামিং এর for loop টা ব্যাবহার করব এবং দেখব কিভাবে সি প্রগ্রামিং দিয়ে ইউজারের কাছ থেকে ইনপুট নিয়ে ততগুলো Even/Odd Number Generate করা যায়।
এটার ভিডিও টিউটরিয়াল ইউটিউবে -
প্রোগ্রামটি বুঝতে কোনো সমস্যা হলে কমেন্ট করবেন।
কোড পার্ট
#include <stdio.h>
main ()
{
int number, i;
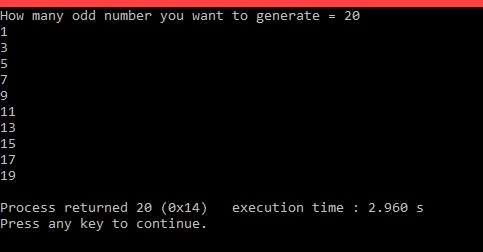
printf("How many odd number you want to generate = ");
scanf("%d", &number);
for(i = 1; i <= number; i = i+2)
{
printf("%d\n", i);
}
}
আউটপুটঃ
ট্যাগসমূহঃ
C program even number bangla tutorial,C program odd number bangla tutorial, c programming bangla tutorials, সি প্রোগ্রাম ভিডিও টিউটোরিয়াল + কোড , সি প্রোগ্রামিং এক্সাম্পল, C programming summation code, C programming subtraction code, C programming even number code, C programming odd number code, C programming code bangla tutorial,Even, Odd Number generate C program Bangla Tutorials - সি প্রোগ্রাম দিয়ে কিভাবে জোড় বিজোড় সংখ্যা বের করা যায় তার প্রোগ্রাম
Summation, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division - সহজ সি প্রোগ্রাম ভিডিও টিউটোরিয়াল + কোড
আজকের টিউটরিয়ালে আমরা দেখব সি প্রোগ্রাম দিয়ে কিভাবে সহজে যোগ, বিয়ো্ গুণ, ভাগের একটি ছোট্ট এবং সহজ প্রোগ্রাম করা যায় ।আজকের সি প্রোগ্রামিং এক্সাম্পলটা একদম সহজ এবং বিগিনার লেভেলের একটি সি প্রোগ্রাম। এই প্রোগ্রামের মাধ্যমে আমরা দেখব কিভাবে সি প্রগ্রামিং দিয়ে ভ্যারিয়েবল ডিক্লিয়ার করে যোগ করতে হয় এবং সাথে ইউজারের কাছ থেকে ইনপুট নিয়ে যোগ করতে হয়।
যেহেতু আমরা জানি যোগ , বিয়োগ, গুণ, ভাগ একই টাইপের সমস্যা, তাই সেগুলাও একইসাথে দেখানো হয়েছে। এটার ভিডিও টিউটরিয়াল ইউটিউবে -
প্রোগ্রামটি বুঝতে কোনো সমস্যা হলে কমেন্ট করবেন।
সি প্রোগ্রামিং এই এক্সাম্পলটির ভিডিও ইউটিউবে দেখুনঃ
ভিডিও লিংক - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tlMU4uDbER0কোড পার্ট
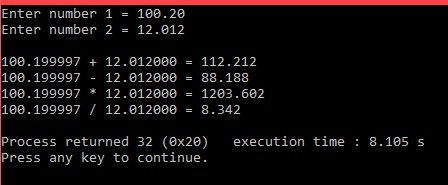
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
float number1, number2, result;
printf("Enter number 1 = ");
scanf("%f", &number1);
printf("Enter number 2 = ");
scanf("%f", &number2);
result = number1+number2;
printf("\n%f + %f = %.3f", number1, number2, result);
result = number1-number2;
printf("\n%f - %f = %.3f", number1, number2, result);
result = number1*number2;
printf("\n%f * %f = %.3f", number1, number2, result);
result = number1/number2;
printf("\n%f / %f = %.3f\n", number1, number2, result);
}
আউটপুটঃ
ট্যাগসমূহঃ
C program summation bangla tutorial, c programming multiplication bangla tutorials, Summation, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division - সি প্রোগ্রাম ভিডিও টিউটোরিয়াল + কোড , সি প্রোগ্রামিং এক্সাম্পল, C programming summation code, C programming subtraction code, C programming multiplication code, C programming division code, C programming code bangla tutorialSummation, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division - সি প্রোগ্রাম ভিডিও টিউটোরিয়াল + কোড
আজকের টিউটরিয়ালে আমরা দেখব সি প্রোগ্রাম দিয়ে কিভাবে সহজে যোগ, বিয়ো্ গুণ, ভাগের একটি ছোট্ট এবং সহজ প্রোগ্রাম করা যায় ।সরাসরি ভিডিও দেখুন ইউটিউবেঃ
কোড পার্ট
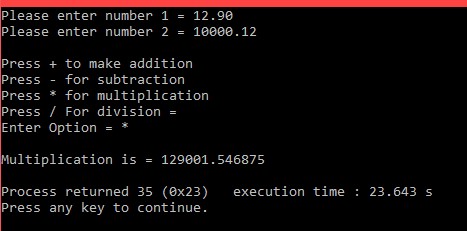
#include<stdio.h>
void main(){
char option;
float number1, number2, result;
printf("Please enter number 1 = ");
scanf("%f", &number1);
printf("Please enter number 2 = ");
scanf("%f", &number2);
printf("\nPress + to make addition\nPress - for subtraction\nPress * for multiplication\nPress / For division = ");
printf("\nEnter Option = ");
scanf(" %c", &option);
if(option == '+'){
result = number1+number2;
printf("\nSummation is = %f\n", result);
}else if(option == '-'){
result = number1-number2;
printf("\nSubtraction is = %f\n", result);
}else if(option == '*'){
result = number1*number2;
printf("\nMultiplication is = %f\n", result);
}else if(option == '/'){
result = number1/number2;
printf("\nDivision is = %f\n", result);
}else{
printf("\nSorry !! You've pressed a wrong button, Try again\n");
}
return 0;
}
আউটপুটঃ
ট্যাগসমূহঃ
Summation, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division - সি প্রোগ্রাম ভিডিও টিউটোরিয়াল + কোড , সি প্রোগ্রামিং এক্সাম্পল, C programming summation code, C programming subtraction code, C programming multiplication code, C programming division code, C programming code bangla tutorialMatlab 13 Codes for Simulation and Modeling
There are most important Matlab codes for Simulation and Modeling Course. These codes are done by me and with some of my friends. Error's are not impossible. See these codes for Simulation and modeling course.
[Having any error, please comment]
- Mid Square Random Number Generator Matlab code
- Residue Method / Mixed Multiplicative Random Number Generator Matlab code
- Additive Congruential Random Number Generator Matlab code
- Multiplicative Congruential Random Number Generator Matlab code
- Arithmetic congruential Method Random Number Generator Matlab code
- Binomial Distribution Matlab code
- Poison Distribution Matlab code
- Chi Square Test for a given set of random numbers
- Monte Carlo - Pure Pursuit Code For Matlab
- Monte Carlo - Gambling Game Code For Matlab
- Monte Carlo - Monte Carlo Integration Code For Matlab
- Monte Carlo - Monte Carlo Pi Code For Matlab
- Single Server Queuing System Matlab Code
Mid Square Method Random Number Generator Code
totalNumber = input('Number of Random Numbers want to generate : ');
choose = input('Enter the seed : ');
disp('Total Random Numbers are : ');
for i = 1:totalNumber
random = choose ^ 2;
random = random / 100; % Find the dividend
random = rem(random, 10000); % Get the reminder;
choose = random;
fprintf('%.2f ', random);
end
fprintf('\n');
Output Mid square random Number generator:
Residue Method / Mixed Multiplicative Random Number Generator Code
clc;
a=input('Please Enter the value of a : ');
b=input('Please Enter the value of b : ');
m=input('Please Enter the value of m : ');
r=input('Please Enter the value of seed or r : ');
totalNumber = input('Number of Random Numbers want to generate : ');
for i = 1:totalNumber
r = mod(a*r +b, m);
fprintf('%4.0f ', r);
end
fprintf('\n');
Output Residue Method random Number generator:
Additive Congruential Method Random Number Generator Code
Same as residue method in this case just a = 1 and hence rules changed
%% r(i+1) = (r(i) + b) mod m
clc;
b=input('Please Enter the value of b : ');
m=input('Please Enter the value of m : ');
r=input('Please Enter the value of seed or r : ');
totalNumber = input('Number of Random Numbers want to generate : ');
for i = 1:totalNumber
r = mod(r +b, m);
fprintf('%4.0f ', r);
end
fprintf('\n');
Output Additive Congruential Method random Number generator:
Multiplicative Congruential Method Random Number Generator Code
Same as residue method in this case just b = 0 and hence rules changed
%% r(i+1) = (ar(i)) mod m
clc;
a=input('Please Enter the value of a : ');
m=input('Please Enter the value of m : ');
r=input('Please Enter the value of seed or r : ');
totalNumber = input('Number of Random Numbers want to generate : ');
for i = 1:totalNumber
r = mod(a*r, m);
fprintf('%4.0f ', r);
end
fprintf('\n');
Output Multiplicative Congruential Method random Number generator:
Arithmetic congruential Random Number Generator Code
%% r(i + 1) = (r(i) + r(i - 1)) percent m
clc;
N = input('Enter How Many Number You want to generate = ');
r0 = input('Enter First Random Number = ');
r1 = input('Enter Second Random Number = ');
m = input('Enter Maximum Range Of Random Number = ');
for i = 1:N
r2 = r0 + r1;
random = mod(r2, m);
fprintf('%d ', random);
r0 = r1;
r1 = r2;
end
Output Arithmetic congruential random Number generator:
Binomial Distribution Code
clc;
trial = input ('Type the number of trial = ');
p = input('Type the value of p(<1.0) the probability of success = ');
variate = input('Type the number of variates to be generated = ');
fprintf('Here,You gave \t Number of trial = %d, Probability of success = %d\nNumber of variates = %d\n',trial,p,variate);
x = 0; n = trial;
for i = 1:n
y = rand();
if(y<p)
x = x+1;
end
fprintf('x = %d\n', x);
end
Output Binomial Distribution :
Poison Distribution Code
clc;
lamda_value = input('Value of Lamda = ');
number_values = input('Number Of Values = ');
for i=1:number_values
count = 0;
p = 0;
fact = 1;
y = rand;
while(y > p)
prob = (power(lamda_value,count)*power(2.718282,-lamda_value))/fact; %Use the poison rules
p = p + prob;
count = count + 1;
fact = fact * count;
end
fprintf('%.f\t',count);
fprintf('\n');
end
fprintf('\n');
Output Poison Distribution :
Chi Square Test for a given set of random numbers Matlab Code
clc;
r = [36 91 51 02 54 06 58 06 58 02 54 01 48 97 43 22 83 25 79 95 42 87 73 17 02 42 95 38 79 29 65 09 55 97 39 83 31 77 17 67 62 03 49 90 37 13 17 58 11 51 92 33 78 21 66 09 54 49 90 35 84 26 74 22 62 12 90 36 83 32 75 31 94 34 87 40 07 58 05 56 22 58 77 71 10 73 23 57 13 36 89 22 68 02 44 99 27 81 26 85 ];
r_length = length(r);
fprintf('Total Students = %d\n', r_length);
for i = 1:r_length
fprintf(' %d ', r(i));
end
fprintf('\n');
Acceptance_value = input('Enter acceptance value at that confidence level = ');
Expected = input('Enter Expected value = ');
E = Expected;
Range = Expected * Expected;
frequency = 0;
diff_square = 0;
i = 0;
while i < Range
for j = 1:r_length
if((r(j) > i) && (r(j) <= Expected))
frequency = frequency + 1;
end
end
O = frequency;
diff_square = diff_square + (abs(O - E)) ^ 2;
fprintf('Difference Square = %d\n', frequency);
i = i + E;
Expected = Expected + E;
frequency = 0;
end
chi_square = double(diff_square / E);
fprintf('\n\nChi Square value is = %f\n', chi_square);
if (Acceptance_value > chi_square)
fprintf('\nThe random numbers follows the chi-square test. Because Chi Square value %.2f is less than Acceptance value %.2f\n', chi_square, Acceptance_value);
else
fprintf('\nThe random numbers follows the chi-square test. Because Chi Square value %.2f is greater than Acceptance value %.2f\n', chi_square, Acceptance_value);
end
fprintf('\n\n');
Output Chi Square Test Code :
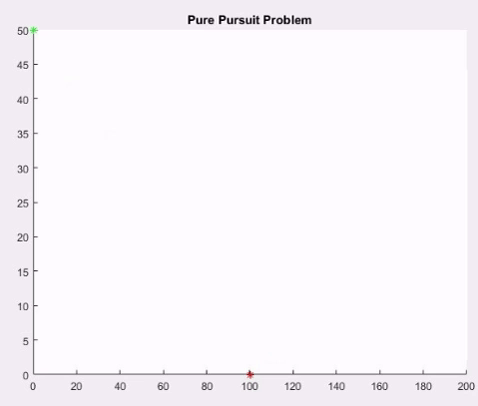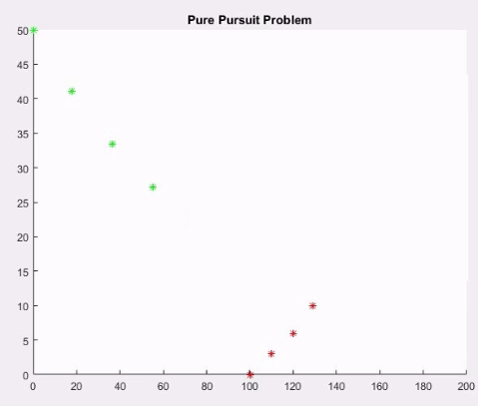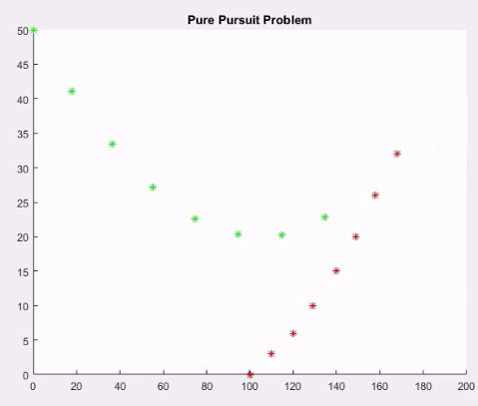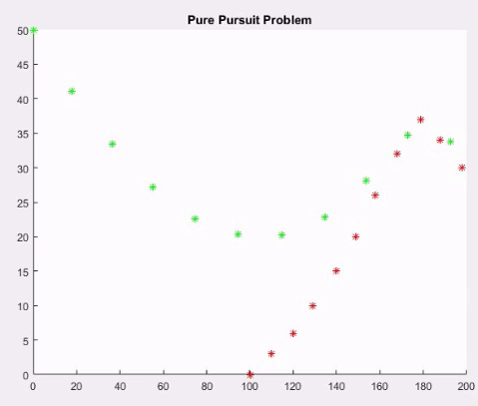
Monte Carlo - Pure pursuit Bombers and Fighters Matlab Code
clc;
hold all;
xb=[100 110 120 129 140 149 158 168 179 188 198 209 219 226 234 240];
yb=[0 3 6 10 15 20 26 32 37 34 30 27 23 19 16 14];
xf = [];
yf = [];
xf(1)=0;
yf(1)=50;
s=20;
dist=0;
for i=1:15
pause on;
plot(xb(i),yb(i),'r*');
title('Pure Pursuit Problem');
pause(1);
plot(xf(i),yf(i),'g*');
y=yb(i)-yf(i);
x=xb(i)-xf(i);
dist=sqrt(y^2+x^2);
if(dist<=12)
fprintf('Bomber destroyed at %d s',i);
break;
end
xf(i+1)=xf(i)+s*((xb(i)-xf(i))/dist);
yf(i+1)=yf(i)+s*((yb(i)-yf(i))/dist);
end
Output Monte Carlo - Pure Pursuit Bombers and fighters Code :
Bomber destroyed at 11 s>>
Gambling Game - Monte Carlo Matlab Code
clc;
n = input('How many time you want to play the game : ');
difference = 0;
tail = 0;
head = 0;
fprintf('\n---------------------------------------------------------------\n');
fprintf('Game No.\tSl No.\tRandom Number\tHeads\tTails\tDifference');
fprintf('\n---------------------------------------------------------------\n');
for i = 1:n
j = 1;
while 1
toss = int8((10-0)*rand(1) + 0); %Generate a random number between 0 to 10%
if (toss > 4)
tail = tail + 1;
else
head = head + 1;
end
difference = abs((head - tail));
fprintf('\n\t%d\t\t%d\t\t\t%d\t\t\t%d\t\t%d\t\t%d\t\t%d', i, j, toss, head, tail, difference);
if(difference == 3) %The rules of the Gambling - If difference = 3 then Count the lose or won coins
result = 8 - j;
if(result < 0)
fprintf('\n\t\tYou lose %d coins\n', abs(result));
else
fprintf('\n\t\tYou won %d coins\n', abs(result));
end
break;
end
j = j + 1;
end % End while
end % End For
Output Gambling Game - Monte Carlo Matlab Code :
Monte Carlo Integration - Monte Carlo Matlab Code
clc;
max_dot = input('How many times do you want to put dot : ');
inside = 0;
a = input('Enter a : ');
b = input('Enter b : ');
h = input('Enter h : ');
%Draw Plot
for x = 1: .01:10
y = x^3;
plot(x,y, 'y.');
hold on;
end
for i = 1:max_dot
x = a + rand * (b-a);
y = rand * h;
if y <= x^3
inside = inside+1;
plot(x,y, 'r.');
else
plot(x,y, 'g.');
end
hold on;
end
integration = (inside/max_dot) * ((b-a) * h);
fprintf('\nIntegration is : %f\n', integration);
Output Monte Carlo Integration - Monte Carlo Matlab Code :
Monte Carlo Pi - Monte Carlo Matlab Code
clc;
maximum_dot = input('How many times want to put Dot : ');
inside = 0;
a = input('Enter a : ');
b = input('Enter b : ');
h = input('Enter h : ');
for i = 1:maximum_dot
x = rand;
y = rand;
if sqrt(x^2 + y^2) <= 1
plot(x,y,'r.');
inside = inside + 1;
else
plot(x,y,'b.');
hold on;
end
end
fprintf('Pi = %f\n', inside / maximum_dot * 4);
Output Monte Carlo Pi - Monte Carlo Matlab Code :
Code - Single Server Queuing System Matlab Code
total=0; busy=0;
%a=randi([0 8],1,8);
a=[.4 1.6 2.1 3.8 4.0 5.6 5.8 7.2];
a_length=length(a);
arr=zeros(a_length);
%d=randi([0 9],1,5);
d=[2.4 3.1 3.3 4.9 8.6];
b=union(a,d);
l=length(b);
a_t=0;d_t=0;q=0;
axis([0 b(length(b))+1 0 length(a)]);
%Queue delay Time
figure(1);
title('Queue Delay Time');
for i=1:l-1
a_m=ismember(a,b(i));
d_m=ismember(d,b(i));
if sum(a_m)>=1
a_t=a_t+1;
end
if sum(d_m)>=1
d_t=d_t+1;
end
dif=a_t-d_t;
if dif>1
rectangle('Position',[b(i) 0 b(i+1)-b(i) dif-1],'FaceColor',[1 0 0]);
arr(dif)=arr(dif)+(b(i+1)-b(i));
end
if dif>0
busy=busy+(b(i+1)-b(i));
end
end
%Server Busy Time
b_t=0;
figure(2);
title('Server Busy Time');
axis([0 b(length(b))+1 0 length(a)]);
for i=1:l-1
a_m=ismember(a,b(i));
d_m=ismember(d,b(i));
if sum(a_m)>=1
b_t=b_t+1;
end
if sum(d_m)>=1
b_t=b_t-1;
end
if b_t>0
rectangle('Position',[b(i) 0 b(i+1)-b(i) 1],'FaceColor',[0 1 0]);
end
end
for i=1:a_length
total=total+arr(i)*(i-1);
end
disp(total);
disp(total/d(length(d)));
disp(busy);
disp(busy/d(length(d)));
Output Single Server Queuing System Matlab Code
Tags:
Mid Square Random Number Generator Matlab code,Residue Method / Mixed, Multiplicative Random Number Generator Matlab code, Additive Congruential Random Number Generator Matlab code, Multiplicative Congruential Random Number Generator Matlab codeArithmetic congruential Method Random Number Generator Matlab code , Binomial Distribution Matlab code, Poison Distribution Matlab code ,Chi Square Test for a given set of random numbers, Monte Carlo - Pure Pursuit Code For Matlab, Monte Carlo - Gambling Game Code For Matlab, Monte Carlo - Monte Carlo Integration Code For Matlab, Monte Carlo - Monte Carlo Pi Code For Matlab, Single Server Queuing System Matlab Code
Gambling Game Code Implementation in Matlab and C - Simulation
Maniruzzaman Akash
December 05, 2017
C Programming
,
Mathematics
,
MatLab Code
,
Simulation and Modeling
Gambling Game Code Implementation in Matlab and C - Simulation
Problem:
Write the gambling game code in Matlab.Logic / Algorithm for Gambling game code:
Initialize head = 0, tail = 0, difference = 0
while (1)
toss the coin and make value from 0 to 10 using reminder
if (toss > 4)
tail = tail + 1
else
head = head + 1
take difference = head - tail
if (difference == 3)
result = 8 - upto_time
if (result < 0)
lose
else
won
else
Gambling game Code in Matlab
clc;
n = input('How many time you want to play the game : ');
difference = 0;
tail = 0;
head = 0;
fprintf('\n---------------------------------------------------------------\n');
fprintf('Game No.\tSl No.\tRandom Number\tHeads\tTails\tDifference');
fprintf('\n---------------------------------------------------------------\n');
for i = 1:n
j = 1;
while 1
toss = int8((10-0)*rand(1) + 0); %Generate a random number between 0 to 10%
if (toss > 4)
tail = tail + 1;
else
head = head + 1;
end
difference = abs((head - tail));
fprintf('\n\t%d\t\t%d\t\t\t%d\t\t\t%d\t\t%d\t\t%d\t\t%d', i, j, toss, head, tail, difference);
if(difference == 3) %The rules of the Gambling - If difference = 3 then Count the lose or won coins
result = 8 - j;
if(result < 0)
fprintf('\n\t\tYou lose %d coins\n', abs(result));
else
fprintf('\n\t\tYou won %d coins\n', abs(result));
end
break;
end
j = j + 1;
end % End while
end % End For
Output Gambling game Code in Matlab
Gambling game Code in C Language
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int tail,head,i,n,j,difference=0,result,toss;
printf("How many time you want to play ? ");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("\n");
tail = 0;
head = 0;
printf("Serial \t Head: \t Tail: \t Difference: \t\n");
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
j = 1;
while(1)
{
// taking random number
toss = rand() % 10;
if(toss > 4)
{
// if(5,6,7,8,9) then tail will increase
tail = tail + 1;
}
else
{
// if(,1,2,3,4) then head will increase
head = head + 1;
}
// difference between head and tail
difference = abs((head - tail));
printf("%d\t%d\t%d\t%d\n",j,head,tail,difference);
if(difference == 3)
{
// counting result suppose the difference match after 10 step then difference = 8-10=2
result = 8 - j;
if(result < 0)
{
// if answer negative then you are in lose this is the amount of losed coin
printf("You lose %d Coin\n",abs(result));
}
else
{
// if answer positive then you are in benefit this is the amount of benefited/win coin
printf("You win %d Coin\n",abs(result));
}
break;
}
// increament the count like serial number
j++;
}
}
return 0;
}
Gambling game Code in C Language Output
Tags:
Gambling Game Code Implementation in Matlab and C - Simulation, Gambling Matlab code, Gambling game C code, gambling game code implementation, gambling gamePure Pursuit Problem Code - Matlab and C code of Pure pursuit problem
What is Pure pursuit:
Pure pursuit is a type of pursuit curve used in aerial combat in which an aircraft pursues another aircraft by pointing its nose directly towards it.
What is mainly Pure pursuit is:
Logic Behind the pure pursuit problem of simulation:- Bomber Aircraft and a Fighter Aircraft are flying in the a horizontal plane.
- Fighter aircraft and bomber aircraft both are moving inside the rectangular range.
- The fighters and bombers have a velocity given, suppose s = 20 in our code.
- When the distance of the Bomber and the Fighter is less than 12 units, it is assumed that the Bomber is shot down or destroyed.
- The distance between this the bombers and fighter follows the distance rule - dist[t] = √( (yb[t]-yf[t])² + (xb[t]-yf[t])² ).
- In matlab the distance will be dist = sqrt(y^2+x^2).
- Look the pure pursuit problem code now and hope it'll clear to you.
Pure Pursuit Problem MatLab Code
clc;
hold all;
xb=[100 110 120 129 140 149 158 168 179 188 198 209 219 226 234 240];
yb=[0 3 6 10 15 20 26 32 37 34 30 27 23 19 16 14];
xf = [];
yf = [];
xf(1)=0;
yf(1)=50;
s=20;
dist=0;
for i=1:15
pause on;
plot(xb(i),yb(i),'r*');
title('Pure Pursuit Problem');
pause(1);
plot(xf(i),yf(i),'g*');
y=yb(i)-yf(i);
x=xb(i)-xf(i);
dist=sqrt(y^2+x^2);
if(dist<=12)
fprintf('Bomber destroyed at %d s',i);
break;
end
xf(i+1)=xf(i)+s*((xb(i)-xf(i))/dist);
yf(i+1)=yf(i)+s*((yb(i)-yf(i))/dist);
end
Pure Pursuit Problem Output - Matlab:
>> Bomber destroyed at 11 s
>>

Pure Pursuit problem in C language:
Code:
#include < stdio.h >
#include < math.h >
#include < stdlib.h >
void main()
{
float xf,yf, xb,yb,d,distance;
int flag=0,
vf=20,
time=0;
randomize();
xf=rand()%1001;
yf=rand()%1001;
xb=rand()%1001;
yb=rand()%1001;
while(flag==0)
{
d= (yb-yf)*(yb-yf)+(xb-xf)*(xb-xf);
distance=sqrt(d);
printf("time=%d xf=%5.2f yf=%5.2f xb=%5.2f yb=%5.2f distance=%5.2f\n\n",time,xf,yf,xb,yb,distance);
if(distance >100)
{
printf("The bomber plain was shot down at %d second\n",time);
flag=1;
}
else if(distance>900)
{
printf("The bomber plane escaped from sight at %d second\n", time);
flag=1;
}
else
{
xf=xf+vf*(xb-xf)/distance;
yf=yf+vf*(yb-yf)/distance;
xb=rand()%1001;
yb=rand()%1001;
time=time+1;
}
}
getch();
}
Output C code Pure Pursuit:
CASE 1: BOMBER IS SHOT DOWN BY FIGHTER time=0 xf=688.00 yf=796.00 xb=366.00 yb=119.00 distance=749.68 time=1 xf=679.41 yf=777.94 xb=563.00 yb=771.00 distance=116.62 time=2 xf=659.45 yf=776.75 xb=419.00 yb=939.00 distance=290.07 time=3 xf=642.87 yf=787.94 xb=87.00 yb=931.00 distance=573.98 time=4 xf=623.50 yf=792.92 xb=960.00 yb=247.00 distance=641.30 time=5 xf=633.99 yf=775.90 xb=197.00 yb=203.00 distance=720.54 time=6 xf=621.86 yf=759.99 xb=799.00 yb=891.00 distance=220.32 time=7 xf=637.94 yf=771.89 xb=207.00 yb=310.00 distance=631.70 time=8 xf=624.30 yf=757.26 xb=193.00 yb=915.00 distance=459.24 time=9 xf=605.52 yf=764.13 xb=311.00 yb=991.00 distance=371.76 time=10 xf=589.67 yf=776.34 xb=816.00 yb=304.00 distance=523.76 time=11 xf=598.31 yf=758.30 xb=804.00 yb=587.00 distance=267.68 time=12 xf=613.68 yf=745.50 xb=122.00 yb=530.00 distance=536.84 time=13 xf=595.36 yf=737.47 xb=924.00 yb=705.00 distance=330.24 time=14 xf=615.27 yf=735.51 xb=100.00 yb=508.00 distance=563.26 time=15 xf=596.97 yf=727.43 xb=48.00 yb=39.00 distance=880.51 time=16 xf=584.50 yf=711.79 xb=990.00 yb=710.00 distance=405.50 time=17 xf=604.50 yf=711.70 xb=523.00 yb=629.00 distance=116.11 time=18 xf=590.46 yf=697.46 xb=894.00 yb=148.00 distance=627.72 time=19 xf=600.13 yf=679.95 xb=463.00 yb=537.00 distance=198.09 time=20 xf=586.29 yf=665.52 xb=308.00 yb=709.00 distance=281.67 time=21 xf=566.53 yf=668.61 xb=488.00 yb=605.00 distance=101.06 time=22 xf=550.99 yf=656.02 xb=107.00 yb=522.00 distance=463.77 time=23 xf=531.84 yf=650.24 xb=305.00 yb=777.00 distance=259.86 time=24 xf=514.38 yf=659.99 xb=250.00 yb=794.00 distance=296.40 time=25 xf=496.54 yf=669.04 xb=448.00 yb=950.00 distance=285.13 time=26 xf=493.14 yf=688.74 xb=252.00 yb=285.00 distance=470.27 time=27 xf=482.88 yf=671.57 xb=623.00 yb=646.00 distance=142.43 time=28 xf=502.56 yf=667.98 xb=640.00 yb=327.00 distance=367.64 time=29 xf=510.03 yf=649.43 xb=357.00 yb=811.00 distance=222.54 time=30 xf=496.28 yf=663.95 xb=623.00 yb=353.00 distance=335.78 time=31 xf=503.83 yf=645.43 xb=156.00 yb=371.00 distance=443.06 time=32 xf=488.13 yf=633.04 xb=533.00 yb=117.00 distance=517.99 time=33 xf=489.86 yf=613.12 xb=301.00 yb=627.00 distance=189.37 time=34 xf=469.91 yf=614.59 xb=143.00 yb=263.00 distance=480.09 time=35 xf=456.29 yf=599.94 xb=780.00 yb=654.00 distance=328.19 time=36 xf=476.02 yf=603.23 xb=928.00 yb=422.00 distance=486.96 time=37 xf=494.58 yf=595.79 xb=757.00 yb=44.00 distance=611.01 time=38 xf=503.17 yf=577.73 xb=734.00 yb=192.00 distance=449.52 time=39 xf=513.44 yf=560.57 xb=49.00 yb=949.00 distance=605.47 time=40 xf=498.10 yf=573.40 xb=515.00 yb=893.00 distance=320.05 time=41 xf=499.16 yf=593.37 xb=111.00 yb=765.00 distance=424.41 time=42 xf=480.87 yf=601.46 xb=463.00 yb=633.00 distance=36.25 The bomber plain was shot down at 42 second CASE 2: BOMBER ESCAPES FROM THE SIGHT OF FIGHTER time=0 xf=642.00 yf=902.00 xb=788.00 yb=709.00 distance=242.00 time=1 xf=654.07 yf=886.05 xb=585.00 yb=997.00 distance=130.69 time=2 xf=643.50 yf=903.03 xb=587.00 yb= 6.00 distance=898.81 time=3 xf=642.24 yf=883.07 xb=11.00 yb=162.00 distance=958.33 The bomber plane escaped from sight at 3 second
Links Where you can learn more on Pure pursuit problem:
- Wikipedia - Pure Pursuit
- Mathworks - Pure Pursuit
Tags:
Pure Pursuit Problem Code - Matlab and C code of Pure pursuit problem, Pure pursuit problem, Pure pursuit problem code, pure pursuit solution in c language, pure pursuit simulation, pure pursuit logic, pure pursuit algorithm, pure pursuit learning, pure pursuit explanation,Single Server Queuing System - MatLab, C, Java code Implementation
Maniruzzaman Akash
December 04, 2017
Computer Programming
,
Mathematics
,
MatLab Code
,
Simulation and Modeling
Single Server Queuing System - MatLab and C code Implementation
What:
A single server queuing system is the waiting lines or queues in that system. A single server queuing system can tell us the following things-- How many times a user need to wait in waiting & Total waiting time
- How many times user take in service time & Total service time
- How many users are in the Queue & Total queue time
- How many users has completed their work in that system yet.

Where Single server queuing system is used
Single server queuing system is applied almost all the fields in real life. Like,- In banking system, taking money from the bank. User needs to stand in a line and take money one by one
- A Bus, plane ticketing system
- Any system with line and who needs to put user in the queue
Real time example of a server queuing system - Patient Data:
 |
| Single Server Queuing Example of patient and doctor |
Single Server Queuing MatLab Code implementation without input (with figure):
Code
total=0; busy=0;
%a=randi([0 8],1,8);
a=[.4 1.6 2.1 3.8 4.0 5.6 5.8 7.2];
a_length=length(a);
arr=zeros(a_length);
%d=randi([0 9],1,5);
d=[2.4 3.1 3.3 4.9 8.6];
b=union(a,d);
l=length(b);
a_t=0;d_t=0;q=0;
axis([0 b(length(b))+1 0 length(a)]);
%Queue delay Time
figure(1);
title('Queue Delay Time');
for i=1:l-1
a_m=ismember(a,b(i));
d_m=ismember(d,b(i));
if sum(a_m)>=1
a_t=a_t+1;
end
if sum(d_m)>=1
d_t=d_t+1;
end
dif=a_t-d_t;
if dif>1
rectangle('Position',[b(i) 0 b(i+1)-b(i) dif-1],'FaceColor',[0 .5 .5]);
arr(dif)=arr(dif)+(b(i+1)-b(i));
end
if dif>0
busy=busy+(b(i+1)-b(i));
end
end
%Server Busy Time
b_t=0;
figure(2);
title('Server Busy Time');
axis([0 b(length(b))+1 0 length(a)]);
for i=1:l-1
a_m=ismember(a,b(i));
d_m=ismember(d,b(i));
if sum(a_m)>=1
b_t=b_t+1;
end
if sum(d_m)>=1
b_t=b_t-1;
end
if b_t>0
rectangle('Position',[b(i) 0 b(i+1)-b(i) 1],'FaceColor',[0 .5 .5]);
end
end
for i=1:a_length
total=total+arr(i)*(i-1);
end
disp(total);
disp(total/d(length(d)));
disp(busy);
disp(busy/d(length(d)));
Output with Figure
(Run the code and wait. Figure will open after 2/3 seconds)
 |
| Matlab Complaete Example - Single Server Queuing system |
Single Server Queuing MatLab Code implementation with input:
N = input('Enter the Value of N: ');
% Variable Declaration
AT = [];
ST = [];
WT = [];
QL = [];
IDT = [];
CAT = [];
CDT = [];
CLK = 0;
% Initialization
AT(1) = 0;
for k = 2:N
AT(k) = input('Enter interarrival time : ');
end
for k = 1:N
ST(k) = input('Enter Service time : ');
end
CAT(1) = AT(1);
CDT(1) = ST(1);
for k = 1:N
WT(k) = 0;
IDT(k) = AT(1);
QL(k) = 0;
end
% Calculation
for i = 2:N
CAT(i) = CAT(i-1) + AT(i);
WT(i) = CDT(i-1) - CAT(i);
if WT(i) < 0
WT(i) = 0;
end
DIF = CAT(i) - CDT(i-1);
if DIF < 0
CDT(i) = CDT(i-1) + ST(i) ;
if i>2
if (CAT(i) < CDT(i-2) || QL(i-1) == 0)
QL(i) = QL(i-1) + 1;
else
QL(i) = QL(i-1);
end
else
QL(i) = QL(i-1) + 1;
end
elseif DIF > 0
CDT(i) = CAT(i) + ST(i) ;
if QL(i-1) > 0
QL(i) = QL(i-1) - 1;
end
else
QL(i) = QL(i-1);
end
if QL(i) == 0
IDT(i) = CAT(i) - CDT(i-1);
end
end
% Display Results
CAT
CDT
WT
IDT
QL
Input data / Output Example for this single server queuing system
Enter the Value of N: 8
Enter interarrival time : 10
Enter interarrival time : 15
Enter interarrival time : 35
Enter interarrival time : 30
Enter interarrival time : 10
Enter interarrival time : 5
Enter interarrival time : 5
Enter Service time : 20
Enter Service time : 15
Enter Service time : 10
Enter Service time : 5
Enter Service time : 15
Enter Service time : 15
Enter Service time : 10
Enter Service time : 10
CAT =
0 10 25 60 90 100 105 110
CDT =
20 35 45 65 105 120 130 140
WT =
0 10 10 0 0 5 15 20
IDT =
0 0 0 15 25 0 0 0
QL =
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 2
>>
Single Server Queuing C Code implementation:
Single Server Queuing system in Java language:
import java.util.Random;
/**
*
* @author Hizbul Bahar
*/
public class SingleServer {
static int Queue_size = 32000;
static int next_event_type;
static int num_custs_delayed;
static int num_events=2;
static int num_in_q;
static int server_status;
static int num_delays_required;
static double area_num_in_q;
static double area_server_status;
static double sim_time;
static double time_last_event;
static double total_of_delays;
static double mean_interarrival;
static double mean_service;
static double[] time_arrival = new double[Queue_size];
static double[] time_next_event=new double[3];
static Random random = new Random(10000);
static void initialize()
{
sim_time = 0;
server_status = 0;
num_in_q = 0;
time_last_event = 0;
num_custs_delayed = 0;
total_of_delays = 0;
area_num_in_q = 0;
area_server_status = 0;
time_next_event[1] = sim_time + expon(mean_interarrival);
time_next_event[2] = 1.0e+30;
}
static void timing()
{
if (time_next_event[1] < time_next_event[2])
next_event_type = 1;
else
next_event_type = 2;
sim_time = time_next_event[next_event_type];
}
static void arrive()
{
double delay;
time_next_event[1] = sim_time + expon(mean_interarrival);
if (server_status == 1)
{
num_in_q++;
time_arrival[num_in_q] = sim_time;
}
else
{
delay = 0;
total_of_delays += delay;
num_custs_delayed++;
server_status = 1;
time_next_event[2] = sim_time + expon(mean_service);
}
}
static void depart()
{
if (num_in_q == 0)
{
server_status = 0;
time_next_event[2] = 1.0e+30;
}
else
{
num_in_q--;
num_custs_delayed++;
time_next_event[2] = sim_time + expon(mean_service);
for (int i = 1; i <= num_in_q; i++)
time_arrival[i] = time_arrival[i+1];
}
}
static void report()
{
System.out.println( "TOtal customer uses this server " + num_custs_delayed + "\n");
System.out.println( "Average delay in queue minutes " + total_of_delays / num_custs_delayed + "\n");
System.out.println( "Average number in queue " + area_num_in_q / sim_time + "\n");
System.out.println( "Server utilization " + area_server_status / sim_time + "\n");
}
static void update_time_avg_stats()
{
double time_since_last_event;
time_since_last_event = sim_time - time_last_event;
time_last_event = sim_time;
area_num_in_q += num_in_q * time_since_last_event;
area_server_status += server_status * time_since_last_event;
}
static double expon(double mean)
{
return -mean * Math.log(random.nextDouble());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
timing();
update_time_avg_stats();
switch (next_event_type)
{
case 1: arrive();
break;
case 2: depart();
}
}
}
Links following to learn single server queuing system
- Wikipedia - Queuing Theory
- A single Server Queuing system.pdf
Tags:
Single Server queuing system example, Single Server Queuing System - MatLab, C, Java code Implementation, Single Server Queuing System Matlab code, Single Server Queuing System C code, Single Server Queuing System java code, Single Server Queuing System matlab code implementation, single server queue, discrete simulation example, single server code and algorithmQuestion is:
What is the block diagram of an Op-amp / Block diagram of an operational amplifier.Solution:
Block Diagram of an operational amplifier is above:There are four stages in any Op-amp. They are
1) Input stage:
Input stage is dual input and balanced output differential amplifier The input stage provides the maximum input gain of the amplifier. It also establishes the input resistance of the op-amp.
2) Intermediate Stage:
Intermediate stage of Op-amp is the output of the first stage. It is dual input unbalanced output.
3) Level Shifting Circuit:
Level shifting circuit is used to shift the DC level at the output. It is the emitter follower using constant current source.
4) Output Stage:
It is the complementary symmetry push-pull amplifier. It increases the output voltage swing and raises the current supplying capability of the op-amp. It provides the low output resistance.
Tags:
Block Diagram of an Op-amp / Block diagram of an operational amplifier, Electrical Electronics, Different stages of op-amp, Operational amplifier
Laplace Transform Derivatives Theorem Proofs - First, Second, Third Order Proofs
Laplace Transform Derivatives First Order Proof:
We'll now find the first order derivatives theorem proof of Laplace transform here:
First Order Derivative theorem is =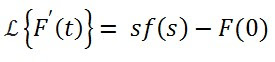

First Order Derivative theorem is =
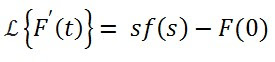
Proof Of First Order Derivative theorem Laplace Transform:

So, by this way we've proved the first order derivatives theorem for Laplace Transform.
Laplace Transform Derivatives Second Order Proof:
We'll now find the second order derivatives theorem proof of Laplace transform here:
If F(t) is a twice differential function of t then
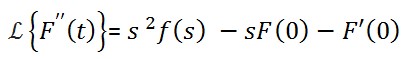

I've written here the complete works , we can also define that we can get one equation from previous Laplace transform theorem. So, we've proved Laplace transform second order derivatives theorem.
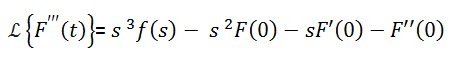

So, now we've proved all of the three basic Laplace Transform Derivatives theorem. Having any problem comment below.
Download Full Tutorial as PDF
If F(t) is a twice differential function of t then
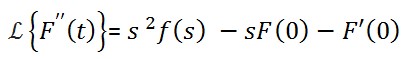
Proof :

I've written here the complete works , we can also define that we can get one equation from previous Laplace transform theorem. So, we've proved Laplace transform second order derivatives theorem.
Laplace Transform Derivatives Third Order Proof:
We'll now find the third order derivatives theorem proof of Laplace transform here:
If F(t) is a thrice differential function of t then
If F(t) is a thrice differential function of t then
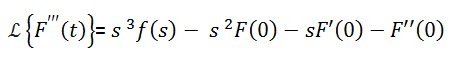
Proof Using Second Order Derivative:
Proof Third Order Full demonstration:
Now get third order derivative a more explained solution or proof

So, now we've proved all of the three basic Laplace Transform Derivatives theorem. Having any problem comment below.
Download Full Tutorial as PDF
Tags:
Laplace Transform Derivatives Theorem Proofs - First, Second, Third Order Proofs, Laplace Transform Derivatives Theorem Proofs First Order, Laplace Transform Derivatives Theorem Second Order derivatives Proof, Laplace Transform Derivatives Third Order Derivative ProofMathematics Book Differential Equation by Kedar Nath Ram Nath Download Link
Book Name : Differential Equation
Book Author : Kedar Nath Ram Nath
Book Download Link : Download From Media Fire via Adf.ly
Book Download Size - 9.5MB
Book Front Page -
So, Download Differential Equation Book By Clicking Download From Media Fire via Adf.ly Button.
Note:
If you have face any problem to download Differential Equation book of Kedar Nath Ram Nath then comment below. A direct link of this book will send to you immediately.Tags:
Mathematics Book Differential Equation by Kedar Nath Ram Nath Download Link, Kedar Nath Ram Nath Book, Differential Equation book pdf, Dr BD Sharma Book PDF Link, Kedar Nath Differential Equation Main book pdf Link
Bash Scripting at a glance - Learn Bash scripting
Take a variable and print out that in Bash Script
Output
name="Akash"
echo "Welcome $name"
Output
Welcome Akash
Take a value From input and test the input using if statement or else do others
#Simple If else in Bash
echo "Please Enter your age : "
read age
if [ $age < 10 ];
then echo "You are really small.."
else
echo "You are growing.."
fi
Print 1 to 100 by for loop using Bash script [Bash Programming Language]
Using seq
# Printing 1 to 100 using for loop
for((i=1;i<=100;i++))
do
echo $i
done
Using seq
for i in `seq 1 100`
do
echo $i
done
Print 0 to 100 even numbers and odd numbers by for loop using Bash script [Bash Programming Language]
0 to 100 even numbers using Bash Scripting
1 to 100 Odd Numbers using Bash scripting
0 to 100 even numbers using Bash Scripting
# Printing 1 to 100 even numbers using for loop
for((i=0;i<=100;i=i+2))
do
echo $i
done
1 to 100 Odd Numbers using Bash scripting
# Printing 1 to 100 odd numbers using for loop
for((i=1;i<=100;i=i+2))
do
echo $i
done
Multiplication program upto 10 using for double for loop Bash scripting [Bash Programming Language]
0 to 100 even numbers using Bash Scripting
Simple Output with Code
Live Link - Live Demo
0 to 100 even numbers using Bash Scripting
# Multiplication Program 1 to 10 in Bash
for((i=1;i<=10;i++))
do
for((j=1;j<=10;j++))
do
echo $i "X" $j "=" $(($i*$j))
done
echo
done
Simple Output with Code
Live Link - Live Demo
Read a file name in Bash and check if file is exist and if file exist, then delete the file, otherwise create the file as new [Bash Programming Language]
search, create, delete a file using Bash Scripting
Explanation :
search, create, delete a file using Bash Scripting
echo "Please Enter your File Name : "
read file_name
if [ -f $file_name ];
then clear
rm $file_name
echo "File $file_name is deleted successfully"
else
clear
touch $file_name
echo "No file found for your search $file_name"
fi
echo "All files are Now : "
ls
Explanation :
- Read the file_name in read file
- Check if file exist in if clause if [ -f $file_name ];
- If Exist then remove the file using rm $file_name.
- If file is not found, create a new file as that name using touch $file_name
- Finally, show the file lists, using ls.
Creating array, inserting value in the array, show the array values and delete the value by searching using Bash script [Bash Programming Language]
echo "How many numbers do you want to add in the array : "
read num
#Take value in the array and put it in a sum variable
arr=() #Empty Array
sum=0
for ((i=0;i<num;i++));
do
echo "Array[$i] = "
read arr[$i]
sum = $((sum+arr[$i]))
done
echo "Summation Is : $sum"
##
# Delete a value from array
##
echo "Please enter a value to delete from the array = "
read delete_value;
for ((i=0;i<num;i++));
do
if [ $((arr[$i])) = $delete_value ]; then
unset arr[$i] #Delete using unset
fi
done
#Show final array
echo "Array is = ${arr[@]}"
Reverse a Number using Bash script [Bash Programming Language]
Reverse a number using bash script in one line :
Why is this : In Bash the integer is also a text. The | reverse any string by that system.
n=123456
rev=0
while [ $n -gt 0 ]
do
reminder=$(( $n % 10 ))
rev=$(( rev*10 + reminder ))
n=$(( $n / 10 ))
done
echo $revReverse a number using bash script in one line :
n=123456
echo $n | revWhy is this : In Bash the integer is also a text. The | reverse any string by that system.
Prime Number check using Bash script [Bash Programming Language]
num=1289
i=2
while [ $i -lt $num ]
do
if [ $(( num%i )) = 0 ];
then
echo "$num is not a prime number"
echo "It is divisible by $i"
exit
fi
$i=$(( i+1 ))
done
echo "$num is a prime number "Tags:
Operating System, Computer Programming, Bash Programming, Bash Scripting at a glance - Learn Bash scripting, file read, delete, create in bash, bash for loop, bash if else, bash loop, bash even numbers, odd numbers using bash
Windows Every Short Command by Windows cmd
First go to command prompt ow windows using cmd.How to see the every command list in windows - windows command:
help
How to see the current directory in windows - windows command:
cd
How to display the directory list in that folder in windows - windows command:
dir
How to create a directory in windows - windows command:
mkdir dir_name
How to remove a directory in windows - windows command:
rmdir dir_name
How to create an empty any types file in windows - windows command:
type NUL > test.txt type NUL > another.c
How to rename a file to new in windows - windows command:
rename test.txt demo.txt
Clear the windows screen - windows command:
cls
Rename multiple files in windows - windows command:
rename *.rtf *.txt
Tags:
Windows Every Short Command by Windows cmd, How to create an empty any types file in windows - windows command, How to remove a directory in windows - windows command, How to create a directory in windows - windows command, How to display the directory list in that folder in windows - windows command, How to see the current directory in windows - windows command
Tutorial on:
FCFS - First Come First Serve Code and Algorithm in C.FCFS - First Come First Serve
First Come First Serve or FCFS is based on First Come First Serve Basis.Algorithm of FCFS:
- Which process comes first to CPU, the process will serve then.
- It is mainly a non preemptive scheduling algorithm. That means, no stop of a process when that's running.
- FCFS implements the First In First Out (FIFO) algorithm. That means which come first to the queue, that will out first from the queue.
C Code of FCFS / First Come First Serve C implementation:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n, burst_time[100], waiting_time[100], turn_around_time[100];
int average_wating_time=0,average_turn_around_time=0;
printf("Total Processes : ");
scanf("%d",&n);
int i, j;
printf("\nEnter Burst Time : \n");
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
printf("P%d = ",i+1);
scanf("%d",&burst_time[i]);
}
waiting_time[0]=0;
for(i=1; i<n; i++)
{
waiting_time[i]=0;
for(j=0; j<i; j++){
waiting_time[i] = waiting_time[i] + burst_time[j];
}
}
printf("\n--------------------------------------------------------------");
printf("\nProcess\t\tBurst Time\tWaiting Time\tTurn around Time");
printf("\n--------------------------------------------------------------\n");
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
turn_around_time[i] = burst_time[i] + waiting_time[i];
average_wating_time += waiting_time[i];
average_turn_around_time += turn_around_time[i];
printf("\nProcess = %d\t\t%d\t\t%d\t\t%d", i+1, burst_time[i], waiting_time[i], turn_around_time[i]);
}
average_wating_time = average_wating_time/n;
average_turn_around_time = average_turn_around_time / n;
printf("\n\nAverage Waiting Time:%d", average_wating_time);
printf("\nAverage Turnaround Time:%d\n\n", average_turn_around_time);
return 0;
}
Output of FCFS:
Explanation of First Come First Serve Algorithm (FCFS)
1) First take the burst time for processes in an array called burst_time[], in these lines, for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
printf("P%d = ",i+1);
scanf("%d",&burst_time[i]);
}2) Then check waiting time. For our first process which waiting time = 0 and for what.
waiting_time[0]=0;3) Then in the waiting_time[] put the waiting times using waiting_time = waiting_time + burst_time for that process. In these lines,
for(i=1; i<n; i++)
{
waiting_time[i]=0;
for(j=0; j<i; j++){
waiting_time[i] = waiting_time[i] + burst_time[j];
}
}4) Then Find the turn around time, average waiting time in these lines,
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
turn_around_time[i] = burst_time[i] + waiting_time[i];
average_wating_time += waiting_time[i];
average_turn_around_time += turn_around_time[i];
printf("\nProcess = %d\t\t%d\t\t%d\t\t%d", i+1, burst_time[i], waiting_time[i], turn_around_time[i]);
}5) Find Average waiting time and average turn around time by dividing the n, in these lines-
average_wating_time = average_wating_time/n;
average_turn_around_time = average_turn_around_time / n;Advantages of FCFS or First Come First Serve Algorithm:
- FCFS is suitable for batch system, basically.
- FCFS is easier to implement.
Disadvantages of FCFS or First Come First Serve Algorithm:
- Waiting time can be large if short request wait for the long process in execution.
- FCFS is not suitable for time sharing system where it is important that each user should get the CPU for equal amount of time interval.
Note:Having any problems in this First Come First Serve algorithm or code, please comment here and don't hesitate.
Tags:
FCFS - First Come First Serve Code in C, Algorithm, Advantage, Disadvantage, FCFS Algorithm, FCFS code in C, FCFS code, FCFS algorithm.
Subscribe to:
Comments
(
Atom
)
































